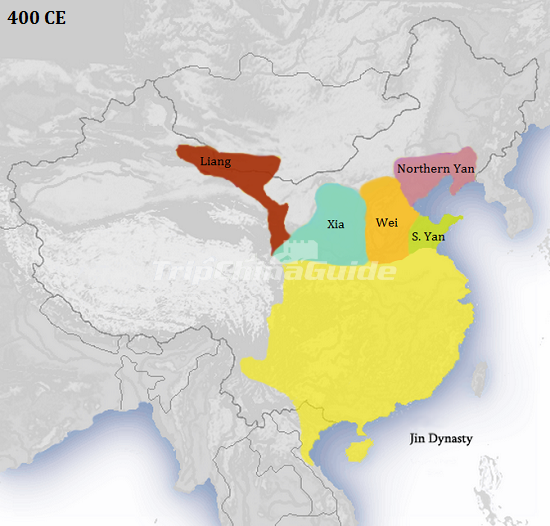
Jin Dynasty
Si-ma Yan began the Jin Dynasty; he ruled from 265-289A.D. As an emperor, he was called Wu Di. The Jin managed to reunify China when, in 280 A.D., they conquered the Wu Kingdom, thus ending the period of The Three Kingdoms. Despite this success, they were not a stable empire. After defeating the Wu, there was no longer a serious danger of being invaded. Therefore, the emperor declared the armies should be disbanded, and all the arms returned. However, this did not occur in every region. The princes, most of whom had been given their titles due to their relationship to the emperor, declared they needed personal guards. The discharged soldiers belonged mainly to the state and didn't give up their weapons either. Instead, they sold them, mainly to the Xiong-nu and the Xian-bei. This was a fatal mistake of the Jin government, as it made them virtually powerless, while all their rivals and enemies gained power.
After the death of Si-ma Yan, there was never again a strong leader. The leaders and princes were often assassinated in the struggle for power. During this time, the Chinese people surrounding the capital suffered due to the fighting and began a migration out from the center of the empire to the more peaceful frontier regions.
The Jin were eventually defeated by the Huns, who claimed they were descendents of the Han Dynasty because of the Han princesses given to them in marriage. However, they never succeeded in forming a true dynasty and uniting China. Rather, the disunity continued with the Northern and Southern dynasties. The defeated Jin fled and from 317-420 they ruled as the Eastern Jin in Nanking.
List of Jin Dynasty Emperors
Jin Dynasty (265–420) Sovereigns | |||||||
Posthumous Names | Birth Name | Years of Reign | Era Name | Range of years | |||
Xi (Western) Jin Dynasty 265-317 | |||||||
Wǔ Dì | 武帝 | Sīmǎ Yán | 司馬炎 | 265-290 | Tàishǐ | 泰始 | 265-274 |
Xiánníng | 咸寧 | 275-280 | |||||
Tàikāng | 太康 | 280-289 | |||||
Tàixī | 太熙 | 290 | |||||
Huì Dì | 惠帝 | Sīmǎ Zhōng | 司馬衷 | 290-306 | Yǒngxī | 永熙 | 290 |
Yǒng pīng | 永平 | 291 | |||||
Yuán kāng | 元康 | 291-299 | |||||
Yǒng kāng | 永康 | 300-301 | |||||
Yǒng níng | 永寧 | 301-302 | |||||
Tàiān | 太安 | 302-303 | |||||
Yǒngān | 永安 | 304 | |||||
Jiànwǔ | 建武 | 304 | |||||
Yǒngān | 永安 | 304 | |||||
Yǒng xīng | 永興 | 304-306 | |||||
Guāngxī | 光熙 | 306 | |||||
Huái Dì | 懷帝 | Sīmǎ Chì | 司馬熾 | 307-311 | Yǒngjiā | 永嘉 | 307-313 |
Mǐn Dì | 愍帝 | Sīmǎ Yè | 司馬鄴 | 313-317 | Jiànxīng | 建興 | 313-317 |
Dong (Eastern) Jin Dynasty 317–420 | |||||||
Yuán Dì | 元帝 | Sīmǎ Ruì | 司馬睿 | 317-322 | Jiànwǔ | 建武 | 317-318 |
Dàxīng | 大興 | 318-321 | |||||
Yǒng chāng | 永昌 | 321-322 | |||||
Míng Dì | 明帝 | Sīmǎ Shào | 司馬紹 | 322-325 | Yǒngchāng | 永昌 | 322-323 |
Tàiníng | 太寧 | 323-325 | |||||
Chéng Dì | 成帝 | Sīmǎ Yǎn | 司馬衍 | 325-342 | Tàiníng | 太寧 | 325 |
Xiánhé | 咸和 | 326-334 | |||||
Xiánkāng | 咸康 | 335-342 | |||||
Kāng Dì | 康帝 | Sīmǎ Yuè | 司馬岳 | 342-344 | Jiànyuán | 建元 | 343-344 |
Mù Dì | 穆帝 | Sima Dān | 司馬聃 | 345-361 | Yǒnghé | 永和 | 345-356 |
Shēng píng | 升平 | 357-361 | |||||
Āi Dì | 哀帝 | Sīmǎ Pī | 司馬丕 | 361-365 | Lónghé | 隆和 | 362-363 |
Xīngníng | 興寧 | 363-365 | |||||
Fèi Dì | 廢帝 | Sīmǎ Yì | 司馬奕 | 365-371 | Tàihé | 太和 | 365-371 |
Jiǎnwén Dì | 簡文帝 | Sīmǎ Yù | 司馬昱 | 371-372 | Xiánān | 咸安 | 371-372 |
Xiāowǔ Dì | 孝武帝 | Sīmǎ Yào | 司馬曜 | 372-396 | Níng kāng | 寧康 | 373-375 |
Tàiyuán | 太元 | 376-396 | |||||
Ān Dì | 安帝 | Sīmǎ Dézōng | 司馬德宗 | 396-418 | Lóngān | 隆安 | 397-401 |
Yuánxīng | 元興 | 402-404 | |||||
Yìxī | 義熙 | 405-418 | |||||
Gōng Dì | 恭帝 | Sīmǎ Déwén | 司馬德文 | 419-420 | Yuánxī | 元熙 | 419-420 |
Recommended China Tour Packages
-
19-day China Buddhist Tour
-
5-day Spotlight on History of Beijing
-
4-day Breathtaking Yellow Mountain Tour